
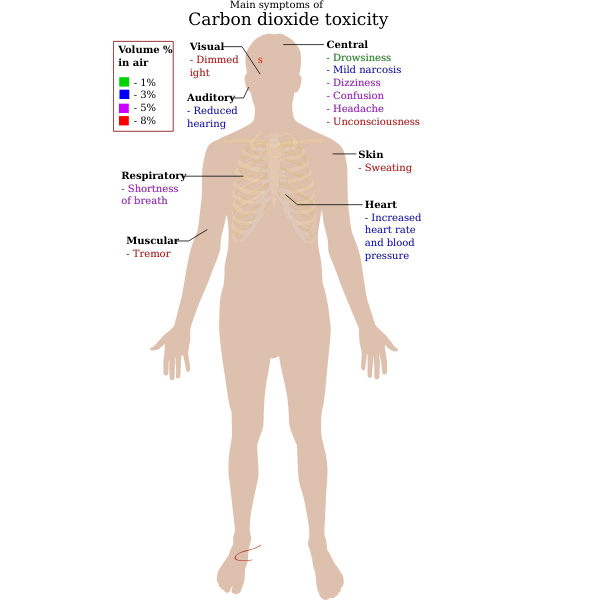
The test may be confounded by use of hydroxocobalamin for treatment of cyanide in smoke inhalation victims.Sample does not need to be kept on ice.The test can be performed on venous or arterial blood.At most hospitals, the only way to obtain a carbon monoxide level is to specifically order this test.Specific laboratory test for carboxyhemoglobin This doesn't measure carbon monoxide levels. However, hospitals are increasingly using point-of-care testing (e.g., iSTAT devices).Some hospitals analyze ABGs and VBGs in a central laboratory, with routine measurement of carbon monoxide and methemoglobin levels in all samples (using spectrophotometry).The ACEP 2017 clinical policy advises using this to diagnose CO toxicity. (2) This isn't adequate for excluding carbon monoxide poisoning, if it is clinically suspected.(1) This is great as a screening tool among undifferentiated emergency department patients.This device is expensive and unavailable at most centers (but will hopefully come down in price eventually). A specifically designed pulse oximeter can detect carbon monoxide by simultaneously measuring absorption at seven wavelengths of light (instead of two, as in most oximeters).MRI reveals hyperintensity on T2/FLAIR sequences, which may eventually resolve over subsequent months (figure above).ĭifferent hospital systems test for carbon monoxide in different ways.Progressive white matter demyelination evolves over weeks following exposure.(2) Delayed leukoencephalopathy may occur in up to a third of patients.Other sites that may be affected include the hippocampi, caudate nuclei, putamina, thalami, cerebellum, corpus callosum, and cerebral cortex.SWI/GRE sequences may reveal hypointensity correlating to hemorrhages.Diffusion restriction is seen on DWI sequences.On T1 sequences, this rim may appear hyperintense. MRI reveals hyperintensity on T2/FLAIR, surrounded by a thin hypointense rim due to hemorrhage.(1) Bilateral, symmetric hemorrhagic necrosis of the globus pallidus:.Over time, CT or MRI scanning may show decreased density in central white matter (e.g., globus pallidus, putamen, and caudate nuclei).Radiologic changes are revealed too late make a substantial impact on management.This is not the preferred mode of diagnosis of CO poisoning!.
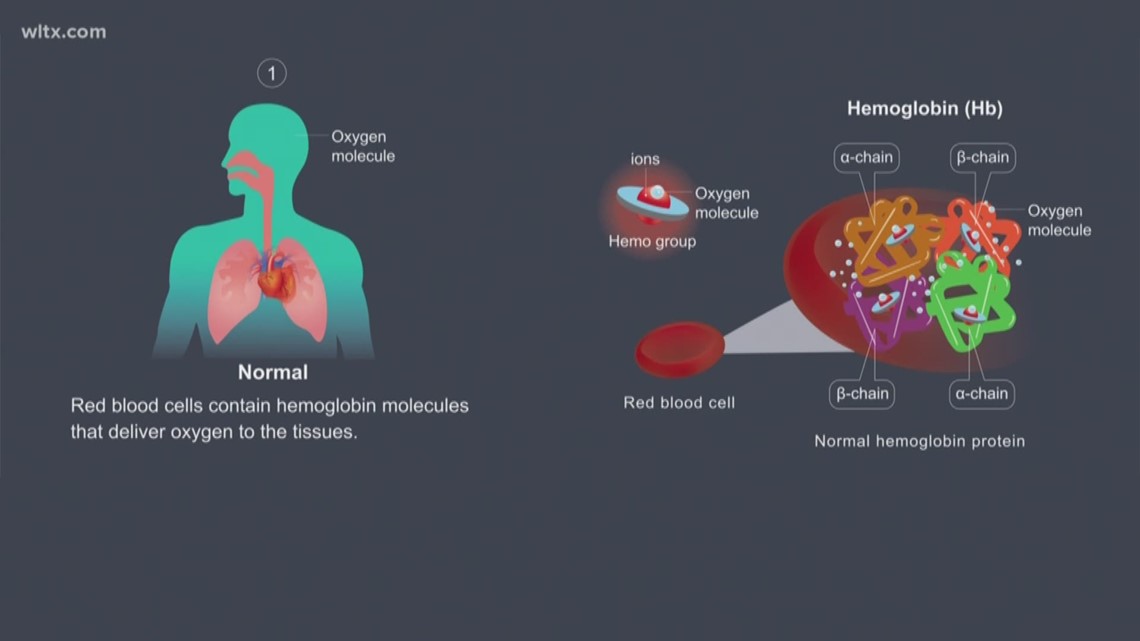
Carboxyhemoglobin levels should be included in the investigation of undifferentiated hyperlactatemia (in patients with potential exposure).CO may increase lactate levels (due to reduced oxygen delivery and impaired tissue oxygen utilization).In practice, this gap will generally be assumed to be a venous blood sample (rather than a true arterial blood specimen).This may be helpful if you stumble over it, but it shouldn't be used intentionally as a diagnostic test for carbon monoxide.This produces a “gap” between the pulse oximetry (which is close to 100%) compared to the PaO2 on ABG (which may be low). Oxygen saturation gap refers to a patient with carbon monoxide poisoning and hypoxemia.Carbon monoxide “tricks” the pulse oximeter into reporting a high oxygen saturation, regardless of what the oxygen saturation actually is.These tests are insensitive, late, and not preferred methods of detecting CO poisoning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
